Lately, vitamin D has been getting a lot of shine. And it’s not just because it’s the “sunshine vitamin.” Health professionals, scientists and experts are bringing more awareness to the importance of vitamin D and its role for optimal health and well-being.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for many bodily functions including strengthening the bones, supporting cell growth and regulation, retaining and absorbing calcium and phosphorus, and improving immunity. Vitamin D is naturally found in some foods and when consumed in excess, it is stored in the body rather than being flushed out through the urine like many other vitamins.
Unfortunately, the majority of Americans aren’t getting enough vitamin D from their diets and as a result many are deficient. Apart from getting vitamin D from food, you might need a little help in keeping your levels in the normal range. Thankfully, with the help of a doctor-approved supplement, you’ll be on your way to better health in no time.
Health Benefits of Vitamin D
Here are six surprising health benefits that will make you want to keep your vitamin D level in check at all times.
1. It supports immunity
Vitamin D does a lot to keep your immune system functioning at its very best. It regulates both the innate and adaptive immune response in the body by interacting with vitamin D receptors on the immune cells and regulating their activity. One study suggests that a deficiency in vitamin D may increase the risk of immune-related diseases. Adequate amounts of vitamin D is needed to help fight off disease-causing germs like viruses, bacteria and parasites.
2. It may help boost your mood
People with depression typically have lower levels of vitamin D, but some studies make it clear that a deficiency doesn’t necessarily cause depression. Individuals that struggle with depression may have a poor appetite, lack of self-care and are more isolated, putting them at risk for vitamin D deficiency. This is because when dealing with depression you may not get adequate nutrition or exposure to sunlight (from being isolated) to keep your vitamin D at healthy levels.
Vitamin D has been shown to increase the production of the “feel good” hormone serotonin, which is responsible for mood regulation and preventing high levels of anxiety and depression. One small study found that vitamin D supplementation in women with type 2 diabetes improved mood and there was a significant decrease in depression and anxiety, but larger studies are needed to confirm this.
3. It might lower the risk of heart disease
Heart disease remains the number one cause of mortality in the nation, therefore it is imperative to do your best to maintain a healthy heart. Like skeletal muscles, heart muscles are regulated when vitamin D interacts with vitamin D receptors in the cells. When it comes to blood pressure, Vitamin D regulates blood pressure by acting on endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Not only that, it has a major role in helping to strengthen muscle fibers, protecting the heart as a result. Additionally, vitamin D may help keep arteries flexible and relaxed, also benefiting blood pressure. Although a deficiency has been linked to various cardiovascular risk factors, more studies are needed to establish the protective role of vitamin D on the heart.
4. It keeps your bones strong
Vitamin D is vital for the health of your bones. Specifically, it enhances the absorption of calcium in the small intestine and stimulates osteoclast (a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue) differentiation and calcium reabsorption of bone. Additionally, vitamin D promotes the mineralization of the collagen matrix in the bone. Vitamin D’s role in calcium absorption and bone health also strengthens the teeth, lowering the risk of tooth decay and gum disease. It’s especially vital for children to have a safe amount of vitamin D for optimal bone health during the bone development stage. In fact, children with low levels of vitamin D are at higher risk of developing a condition called rickets, which leads to bone weakness and other skeletal deformities.
5. It might give you an energy boost
If you are constantly fatigued, getting more vitamin D might give you the energy boost you need. Vitamin D has an impact on the function of the mitochondria, the part of a cell that produces energy. A 2016 study found that vitamin D treatment significantly improved fatigue in healthy people with vitamin D deficiency. Another study suggests that vitamin D supplementation might improve fatigue in kidney transplant recipients.
6. It supports female sex hormones
Vitamin D deficiency is extremely common in reproductive aged women. Recent studies suggest that vitamin D plays an essential role in helping to regulate female sex hormones and that low vitamin D levels can increase the risk for adverse maternal and fetal health outcomes. Additionally, low levels of vitamin D are involved in the development of specific hormone disorders including polycystic ovarian syndrome (a condition in which there is an imbalance of sex hormones) which affects five million women in the United States. If you struggle with PMS symptoms, the good news is that getting enough vitamin D may reduce symptoms, according to a systematic review. There may be some beneficial effects of vitamin D supplementation on clinical pregnancy and fertility outcomes, but results remain inconsistent and more studies are needed to support the claims.
Main Forms of Vitamin D
There are two main forms of vitamin D: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). There’s not much of a difference between the two except that D2 is naturally found in plants and D3 is naturally found in animals and produced by the skin when exposed to sunlight.
Vitamin D is also classified by its measured form 25-OH-Vit D (from the kidneys) and its active form calcitriol (from the liver). The great news is you can meet your vitamin D needs with either form of vitamin D, but most health experts recommend vitamin D3 supplements because it’s more effective in raising vitamin D levels compared to vitamin D2. Plus, it lasts longer in the body.
Top Vitamin D Food Sources
By now you know the importance of getting enough vitamin D in your diet for better health. Here are the top vitamin D rich foods you’ll need to add to keep your levels up to par:
- Cod liver oil (34 mcg per 1 tablespoon serving)
- Salmon (14.2 mcg per 3 oz serving)
- Mushrooms (9.2 mcg per ½ cup serving)
- Fortified milk (2.9 mcg per 1 cup serving) and milk alternatives (2.5-3.6 mcg per 1 cup serving)
- Fortified orange juice (2.5mcg per 1 cup serving)
- Fortified cereal (2.0 mcg per 1 cup serving)
- Beef liver (1.0 mcg per 3 oz serving)
Vitamin D Supplements vs. Food
When it comes to vitamin D, there are a few foods that naturally contain it, although some foods are fortified with vitamin D, like orange juice, milk or some cereals. It’s always best to get your nutrients from food first as it’s more potent, but sometimes it can be challenging to rely on food alone. Healthcare providers may recommend a supplement to help you meet your daily vitamin D requirements and ensure your levels are within normal range. The key is to not overdo it.
Vitamin D supplements are generally safe to take, but excessive consumption can result in hypercalcemia, a condition where calcium becomes too high in the bloodstream, leading to gastrointestinal issues, weakness and kidney stones. Vitamin D supplementation is also generally recommended for people with fat absorption issues, lactose intolerance, milk allergies or for people with certain medical conditions that prevent them from going outdoors. When taking a supplement, you’ll want to take it with a meal to enhance the absorption.
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Fatigue
- Mood changes
- Muscle pain and weakness
- Reduced immune function
- Increased inflammation
- Frequent infections
- Rickets (in children)
- Bone disorders
If you have vitamin D deficiency, which is determined through a blood test, the treatment is typically through supplementation. Check with your healthcare provider about the dose, how often you need to take it and how long you should take it for.
Who is at risk for a vitamin D deficiency?
Melanin is one of the primary factors that affect the synthesis of vitamin D through skin exposure to sunlight. As a result, people of color with darker skin tones are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency as their body is not able to produce vitamin D properly. Individuals at higher risk for deficiency include the elderly, those with minimal exposure to sunlight and people who avoid dairy or fatty fish.
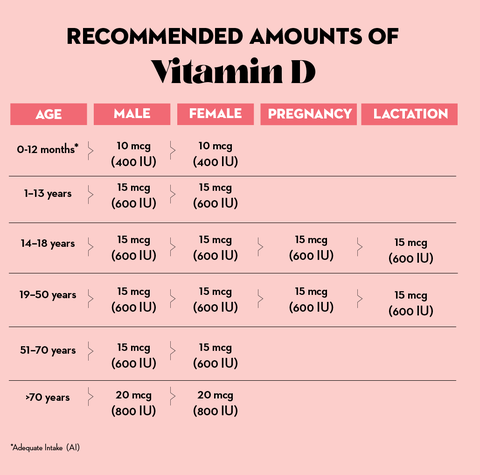
Recommended Vitamin D Amounts
Most people need about 600 IU per day, but people over the age of 70 need a little more, somewhere around 800 IU to reduce the risk of common bone disorders, like osteoporosis, a disease that weakens the bones. Talk to your healthcare provider today about your vitamin D level.
Valerie Agyeman (she/her) is a women’s health dietitian and the host of the Flourish Heights podcast, where she produces science-driven content covering overlooked nutrition, wellness and women’s health topics. She has over 10 years of nutrition communications, corporate wellness and clinical nutrition experience. Valerie is a trusted expert and regularly appears on networks including ABC’s Good Morning Washington, and she is a contributing expert to publications like Women’s Health, The Thirty and Shape.